Symptoms of Patent Ductus Arteriosus
The Causes for Patent Ductus Arteriosus
Risk Factors Associated with Patent Ductus Arteriosus
Complications That May Arise with Patent Ductus Arteriosus
Prevention for Patent Ductus Arteriosus
Come to Doctor Arun’s Clinic for Patent Ductus Arteriosus
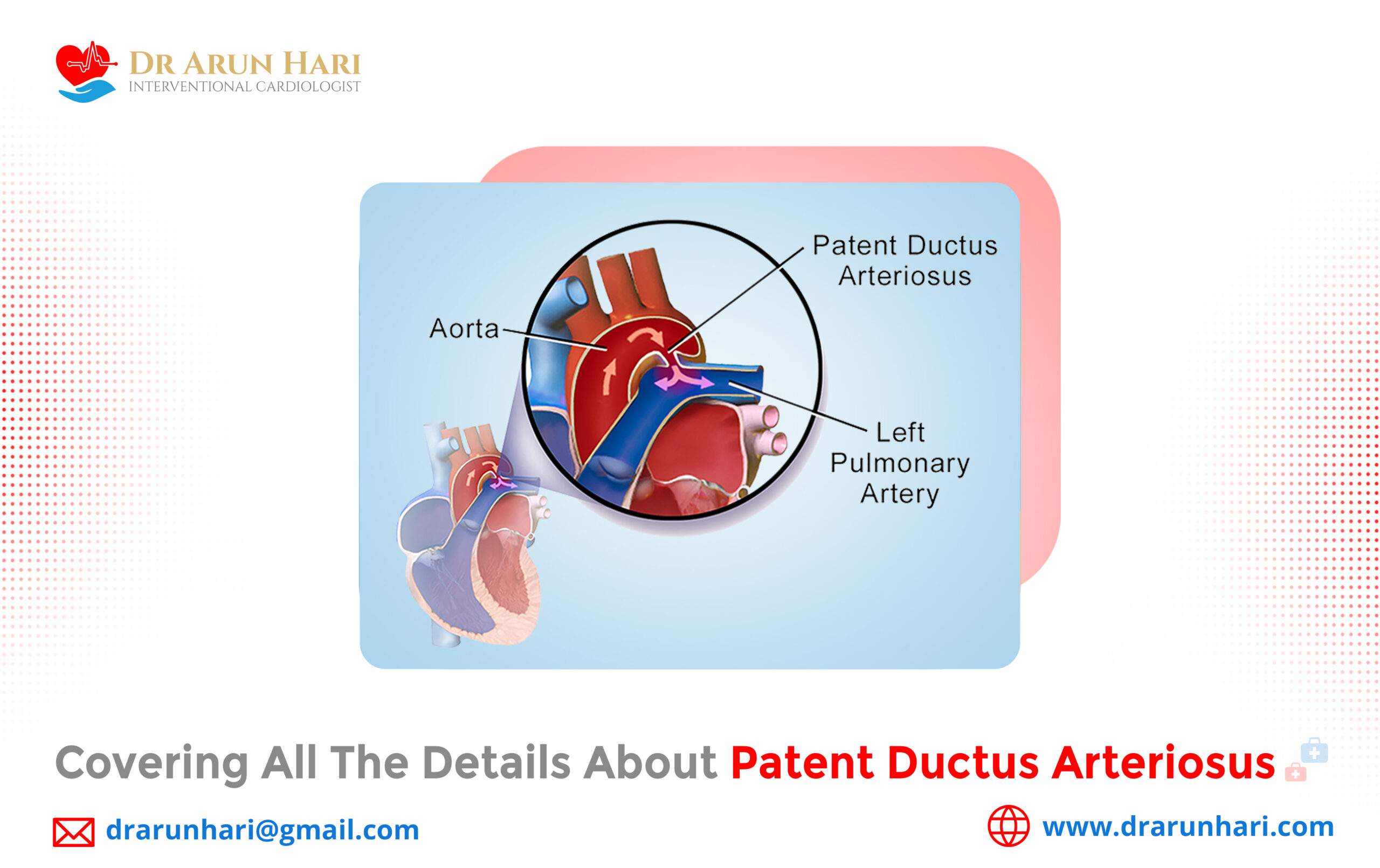
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is a congenital heart defect that occurs when a small blood vessel called the ductus arteriosus, which connects the pulmonary artery to the aorta in a developing fetus, fails to close after birth. This results in the flow of oxygen-rich blood from the aorta into the pulmonary artery and lungs, causing the heart to work harder than normal. If left untreated, PDA can lead to serious complications such as heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, and infective endocarditis.
Symptoms of Patent Ductus Arteriosus
The symptoms can vary depending on the size of the ductus arteriosus and the age of the child. In some cases, PDA may not cause any symptoms and may go undetected until later in life. Still, some of the most commonly seen symptoms include the ones given below:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Shortness of breath
- Rapid breathing
- Rapid heart rate
- Sweating, especially during feedings
- Poor weight gain
- Recurrent respiratory infections
When to See a Doctor
If your child is experiencing any of the above symptoms, it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible. Early diagnosis and treatment of PDA can prevent serious complications and improve the child’s overall health.
The Causes for Patent Ductus Arteriosus
The exact cause is unknown. What is known to date is that PDA happens to be a congenital heart defect that occurs when the ductus arteriosus, a small blood vessel that connects the pulmonary artery to the aorta in a developing fetus, fails to close after birth. Normally, the ductus arteriosus closes within a few days of birth, allowing blood to flow from the aorta to the body and from the pulmonary artery to the lungs.
Risk Factors Associated with Patent Ductus Arteriosus
Some factors that increase the risk of developing Patent ductus arteriosus include:
- Premature birth
- Family history of heart defects
- Certain genetic conditions such as Down syndrome
- Getting exposed to some of the drugs and/or toxins at the time of pregnancy
Complications That May Arise with Patent Ductus Arteriosus
If left untreated, it can lead to serious complications such as:
- Heart failure
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Infective endocarditis
- Eisenmenger syndrome, a rare condition that occurs when the PDA causes irreversible damage to the lungs.
Prevention for Patent Ductus Arteriosus
There is no known way to prevent Patent ductus arteriosus. However, pregnant women can reduce the risk of their child developing PDA by:
- Getting regular prenatal care
- Limiting or completely avoiding the intake of alcohol, tobacco, & other such harmful drugs at the time of pregnancy
- Controlling chronic health conditions such as diabetes or high blood pressure
Come to Doctor Arun’s Clinic for Patent Ductus Arteriosus
In conclusion, Patent ductus arteriosus is a congenital heart defect that happens to occur in the case where the ductus arteriosus somehow fails to close after the birth of a child. This can possibly lead to serious complications if left untreated. Symptoms of PDA include fatigue, shortness of breath, and rapid heart rate. If you see that your child has been experiencing any of such symptoms of PDA, then it’s highly crucial that you see a doctor at the earliest. While there is no known way to prevent PDA, pregnant women can reduce the risk of their child developing PDA by getting regular prenatal care and avoiding alcohol, tobacco, and other drugs during pregnancy. You can come to Doctor Arun’s clinic to understand the condition better and seek proper guidance in this regard.