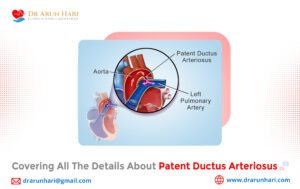
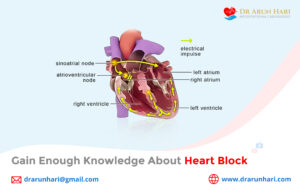
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately 12.1 million people in the U.S. are projected to have atrial fibrillation (AFib) by 2030. This staggering statistic highlights the importance of understanding atrial flutter vs fibrillation, as both conditions can lead to severe cardiovascular complications if left untreated. Dr. Arun Hari, a leading interventional cardiologist, specializes in diagnosing and treating these rhythm disorders using advanced cardiac care techniques.
Understanding the Difference Between Atrial Flutter and Fibrillation
Both conditions are types of atrial arrhythmias, but they differ significantly in their electrophysiological mechanisms and clinical presentation. The difference between atrial flutter and fibrillation lies primarily in the nature of the atrial impulses.- Atrial flutter: Characterized by a rapid but organized electrical impulse, typically leading to a sawtooth pattern on an ECG.
- Atrial fibrillation: Marked by chaotic, uncoordinated atrial electrical activity, resulting in an irregularly irregular heartbeat.
Atrial Fibrillation and Flutter Definition
To understand these conditions better, let’s look at the atrial fibrillation and flutter definition: Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): A supraventricular arrhythmia where the atria experience chaotic electrical signals, causing the heart to beat irregularly and often too fast. Atrial Flutter: A reentrant circuit within the right atrium that causes a rapid but regular rhythm, often at a rate of 250-350 beats per minute.Key Features of Flutter vs Fibrillation on ECG
One of the most effective diagnostic tools for distinguishing flutter vs fibrillation is the electrocardiogram (ECG). Understanding how these conditions appear on an ECG can be crucial for proper diagnosis and management.Atrial Fibrillation on an ECG
Identifying atrial fibrillation on an ECG involves recognizing the following characteristics:- Absence of distinct P waves
- Irregular R-R intervals
- Fibrillatory waves (f waves) replacing P waves
ECG Findings of Atrial Fibrillation
The most notable ECG findings of atrial fibrillation include rapid, erratic atrial electrical activity with no discernible pattern. This contrasts with atrial flutter, which exhibits organized reentrant circuits.Why Early Detection and Treatment Matter
Without timely intervention, both conditions can increase the risk of stroke, heart failure, and other serious complications. Dr. Arun Hari employs cutting-edge treatment methods, including catheter ablation, anticoagulation therapy, and advanced rhythm control strategies, to manage these arrhythmias effectively.Auricular Flutter: A Less Common but Important Consideration
Another term often associated with atrial arrhythmias is auricular flutter, which refers to similar reentrant circuits but can have subtle differences in origin and presentation. Understanding these variations helps in precise diagnosis and treatment.To Summarize
Understanding atrial flutter vs fibrillation is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management. With advancements in cardiology, patients have access to superior treatment options, including those offered by renowned interventional cardiologist Dr. Arun Hari. If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms such as palpitations, dizziness, or an irregular heartbeat, seeking expert medical advice is imperative.FAQs on Atrial Flutter and Fibrillation
1: What is the main cause of AFib vs a flutter?
Both conditions arise from abnormal electrical signals in the atria. While atrial fibrillation is commonly associated with hypertension, valvular heart disease, and aging, atrial flutter often occurs in patients with prior heart surgery, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or congenital heart defects.
2: How can you tell the difference between atrial flutter and fibrillation on an ECG?
The hallmark sign of atrial flutter is a “sawtooth” pattern in the P waves, whereas atrial fibrillation appears as erratic, disorganized fibrillatory waves with irregular ventricular response.
3: What are the treatment options offered by Dr. Arun Hari?
Dr. Arun Hari provides state-of-the-art treatments, including:
Medications: Rate control and rhythm control drugs
Catheter Ablation: Minimally invasive procedure targeting faulty electrical pathways
Anticoagulation Therapy: To prevent stroke risks in AFib patients
Cardioversion: Electrical shock therapy to restore normal rhythm
Medications: Rate control and rhythm control drugs
Catheter Ablation: Minimally invasive procedure targeting faulty electrical pathways
Anticoagulation Therapy: To prevent stroke risks in AFib patients
Cardioversion: Electrical shock therapy to restore normal rhythm
4: Can auricular flutter turn into AFib?
Yes, in some cases, untreated atrial flutter can progress into atrial fibrillation, which may increase the risk of stroke and heart failure.